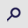
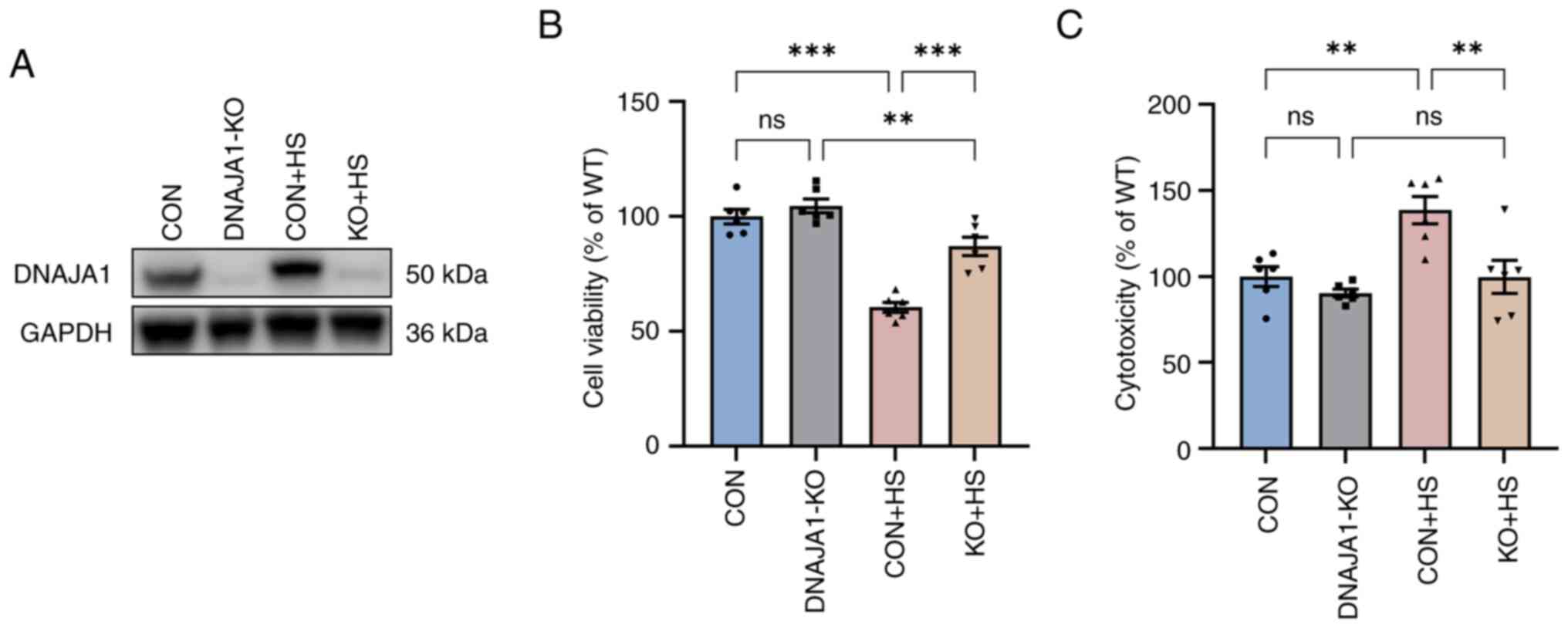
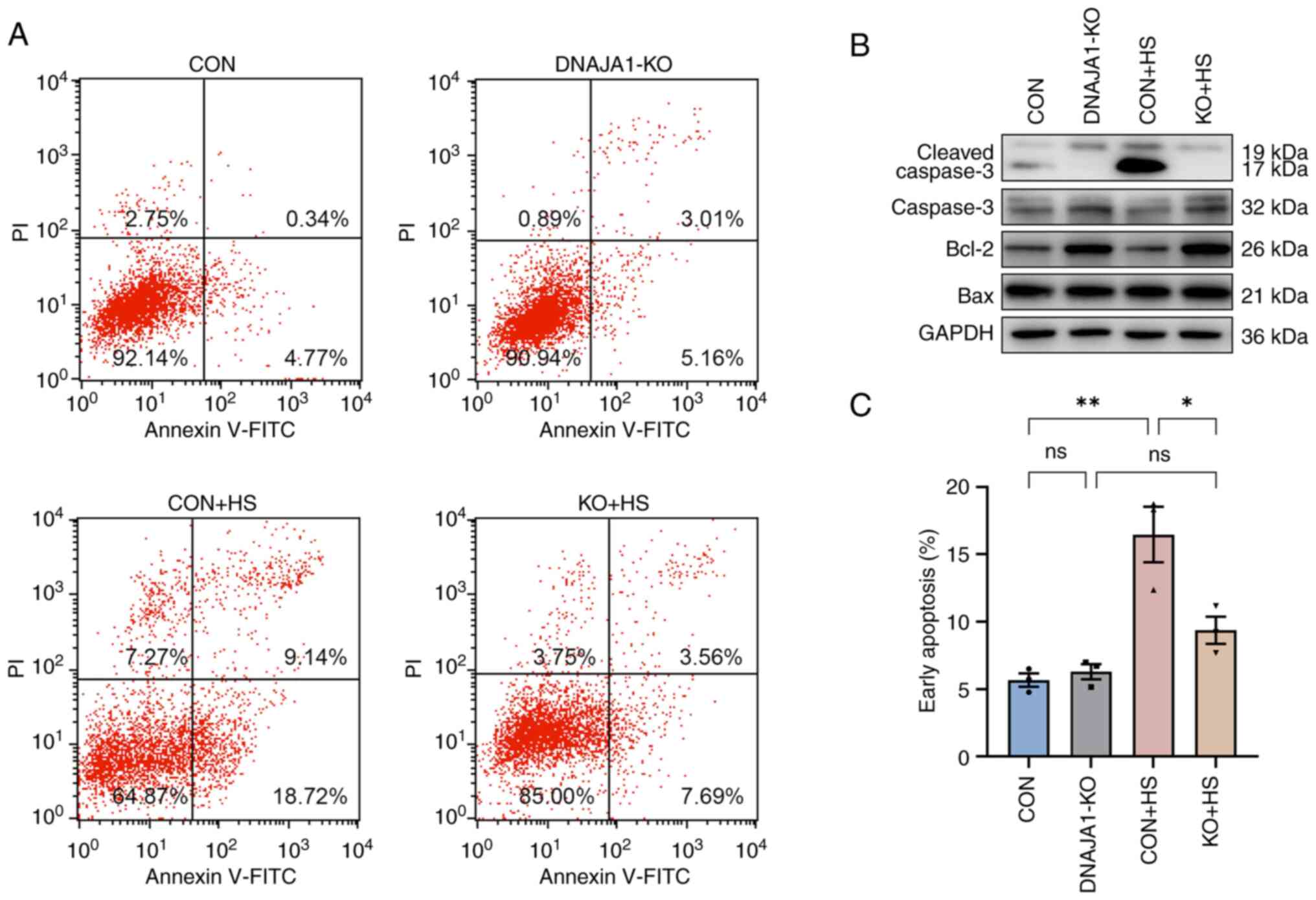
|
1
|
Bouchama A, Abuyassin B, Lehe C, Laitano
O, Jay O, O'Connor FG and Leon LR: Classic and exertional
heatstroke. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 3:82022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Epstein Y and Yanovich R: Heatstroke. N
Engl J Med. 380:2449–2459. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Raymond C, Matthews T and Horton RM: The
emergence of heat and humidity too severe for human tolerance. Sci
Adv. 6:eaaw18382020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fujimoto M and Nishiura H: Baseline
scenarios of heat-related ambulance transportations under climate
change in Tokyo, Japan. PeerJ. 10:e138382022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Aird WC: Endothelium as an organ system.
Crit Care Med. 32:S271–S279. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cheng JL and MacDonald MJ: Effect of heat
stress on vascular outcomes in humans. J Appl Physiol (1985).
126:771–781. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Iba T, Connors JM, Levi M and Levy JH:
Heatstroke-induced coagulopathy: Biomarkers, mechanistic insights,
and patient management. EClinicalMedicine. 44:1012762022.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xu Q, Liu J, Wang Z, Guo X, Zhou G, Liu Y,
Huang Q and Su L: Heat stress-induced disruption of endothelial
barrier function Is via PAR1 signaling and suppressed by Xuebijing
injection. PLoS One. 10:e01180572015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shi J, Zhao Y, Wang K, Shi X, Wang Y,
Huang H, Zhuang Y, Cai T, Wang F and Shao F: Cleavage of GSDMD by
inflammatory caspases determines pyroptotic cell death. Nature.
526:660–665. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang S: Genome-wide CRISPR/Cas9 library
screening identified DNAJA1 regulating protein homeostasis in heat
stress injury, master's dissertation. Naval medical university;
2023
|
|
11
|
Ergulen E, Becsi B, Csomos I, Fésüs L and
Kanchan K: Identification of DNAJA1 as a novel interacting partner
and a substrate of human transglutaminase 2. Biochem J.
473:3889–3901. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Qiu XB, Shao YM, Miao S and Wang L: The
diversity of the DnaJ/Hsp40 family, the crucial partners for Hsp70
chaperones. Cell Mol Life Sci. 63:2560–2570. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kurop MK, Huyen CM, Kelly JH and Blagg
BSJ: The heat shock response and small molecule regulators. Eur J
Med Chem. 226:1138462021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Joshi AD, Dimitropoulou C, Thangjam G,
Snead C, Feldman S, Barabutis N, Fulton D, Hou Y, Kumar S, Patel V,
et al: Heat shock protein 90 inhibitors prevent LPS-induced
endothelial barrier dysfunction by disrupting RhoA signaling. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 50:170–179. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Ren Y, Yu G, Shi C, Liu L, Guo Q, Han C,
Zhang D, Zhang L, Liu B, Gao H, et al: Majorbio cloud: A one-stop,
comprehensive bioinformatic platform for multiomics analyses.
iMeta. 1:e122022. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Health NIO, . Guide for the care and use
of laboratory animals. National Academies; 1985
|
|
17
|
Li L, Man W, Chen J, Xu Z, Wang S, Xia X,
Liu D, Wang S, Xie C, Wu J, et al: Preventive effects of bacillus
licheniformis on heat stroke in rats by sustaining intestinal
barrier function and modulating gut microbiota. Front Microbiol.
12:5482021.
|
|
18
|
Gu ZT, Li L, WU F, Zhao P, Yang H, Liu YS,
Geng Y, Zhao M and Su L: Heat stress induced apoptosis is triggered
by transcription-independent p53, Ca2+ dyshomeostasis and the
subsequent Bax mitochondrial translocation. Sci Rep. 5:114972015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gu ZT, Wang H, Li L, Liu YS, Deng XB, Huo
SF, Yuan FF, Liu ZF, Tong HS and Su L: Heat stress induces
apoptosis through transcription-independent p53-mediated
mitochondrial pathways in human umbilical vein endothelial cell.
Sci Rep. 4:44692015. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang S, Liu Y, Wang Z, Liu J, Gu Z, Xu Q
and Su L: PAR1-mediated c-Jun activation promotes heat
stress-induced early stage apoptosis of human umbilical vein
endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 15:2595–2603. 2017. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wang Y, Yang C, Elsheikh N, Elsheikh NAH,
Li C, Yang F, Wang G and Li L: HO-1 reduces heat stress-induced
apoptosis in bovine granulosa cells by suppressing oxidative
stress. Aging (Albany NY). 11:5535–5547. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Dalal PJ, Muller WA and Sullivan DP:
Endothelial cell calcium signaling during barrier function and
inflammation. Am J Pathol. 190:535–542. 2020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Claesson-Welsh L, Dejana E and McDonald
DM: Permeability of the endothelial barrier: Identifying and
reconciling controversies. Trends Mol Med. 27:314–331. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Clarke JP and Mearow KM: Cell stress
promotes the association of phosphorylated HspB1 with F-actin. PLoS
One. 8:e689782013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yin B, Tang S, Xu J, Sun J, Zhang X, Li Y
and Bao E: CRYAB protects cardiomyocytes against heat stress by
preventing caspase-mediated apoptosis and reducing F-actin
aggregation. Cell Stress Chaperones. 24:59–68. 2019. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Dzwinel W, Boryczko K and Yuen DA: A
discrete-particle model of blood dynamics in capillary vessels. J
Colloid Interface Sci. 258:163–173. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Joffre J and Hellman J: Oxidative Stress
and endothelial dysfunction in sepsis and acute inflammation.
Antioxid Redox Signal. 35:1291–1307. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Iba T, Helms J, Levi M and Levy JH:
Thromboinflammation in acute injury: Infections, heatstroke, and
trauma. J Thromb Haemost. 22:7–22. 2023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liu Z, Zhong T, Zheng D, Cepinskas I, Peng
T and Su L: Heat stress pretreatment decreases
lipopolysaccharide-induced apoptosis via the p38 signaling pathway
in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep.
14:1007–1013. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Huang W, Mao L, Xie W, Cai S, Huang Q, Liu
Y and Chen Z: Impact of UCP2 depletion on heat stroke-induced
mitochondrial function in human umbilical vein endothelial cells.
Int J Hyperthermia. 39:287–296. 2022. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wu F, Dong XJ, Zhang HQ, Li L, Xu QL, Liu
ZF, Gu ZT and Su L: Role of MnSOD in propofol protection of human
umbilical vein endothelial cells injured by heat stress. J Anesth.
30:410–419. 2016. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu Y, Zhou G, Wang Z, Guo X, Xu Q, Huang
Q and Su L: NF-κB signaling is essential for resistance to heat
stress-induced early stage apoptosis in human umbilical vein
endothelial cells. Sci Rep. 5:135472015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Antonov A, Snead C, Gorshkov B, Antonova
GN, Verin AD and Catravas JD: Heat shock protein 90 inhibitors
protect and restore pulmonary endothelial barrier function. Am J
Respir Cell Mol Biol. 39:551–559. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yuan X, Chen Y, Chen G, Liu G, Hang M,
Wang P, Luo Y, Guo D and Xu L: The heat shock protein 70 plays a
protective role in sepsis by maintenance of the endothelial
permeability. Biomed Res Int. 2020:21940902020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Bi J, Zhang J, Ren Y, Du Z, Zhang Y, Liu
C, Wang Y, Zhang L, Shi Z, Wu Z, et al: Exercise hormone irisin
mitigates endothelial barrier dysfunction and microvascular
leakage-related diseases. JCI Insight. 5:e1362772020. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang Z, Lu YL, Chen M, Xu HF and Zheng LR:
Piceatannol alleviates glucolipotoxicity induced vascular barrier
injury through inhibition of the ROS/NF-kappa B signaling pathway.
Am J Transl Res. 14:120–134. 2022.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Du L, Dong F, Guo L, Hou Y, Yi F, Liu J
and Xu D: Interleukin-1beta increases permeability and upregulates
the expression of vascular endothelial-cadherin in human renal
glomerular endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 11:3708–3714. 2015.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hohmann T and Dehghani F: The
cytoskeleton-A complex interacting meshwork. Cells. 8:3622019.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Liu R, Niu X, Yuan J, Chen H, Gao X and Qi
R: DnaJA4 is involved in responses to hyperthermia by regulating
the expression of F-actin in HaCaT cells. Chin Med J (Engl).
134:456–462. 2021. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Wettstein G, Bellaye PS, Micheau O and
Bonniaud P: Small heat shock proteins and the cytoskeleton: An
essential interplay for cell integrity? Int J Biochem Cell Biol.
44:1680–1686. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Almeida-Souza L, Asselbergh B, D'Ydewalle
C, Moonens K, Goethals S, de Winter V, Azmi A, Irobi J, Timmermans
JP, Gevaert K, et al: Small heat-shock protein HSPB1 mutants
stabilize microtubules in charcot-marie-tooth neuropathy. J
Neurosci. 31:15320–15328. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Kayser J, Haslbeck M, Dempfle L, Krause M,
Grashoff C, Buchner J, Herrmann H and Bausch AR: The small heat
shock protein Hsp27 Affects assembly dynamics and structure of
keratin intermediate filament networks. Biophys J. 105:1778–1785.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Du L, Zhu L, Lu X, Yu Y, Liu P and Pan J:
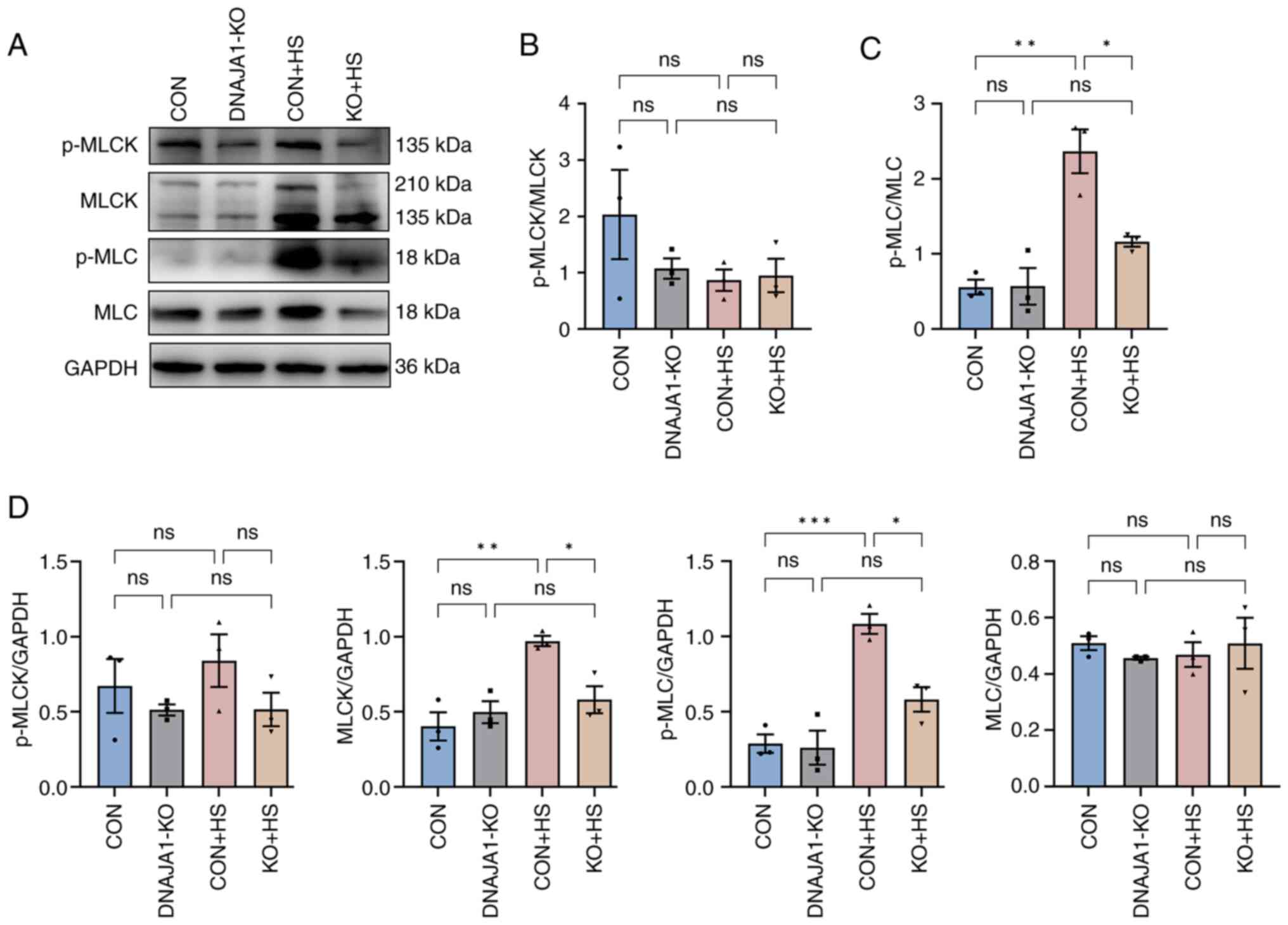
Inhibition of the MLCK/MLC2 pathway protects against intestinal
heat stroke-induced injury in rats. J Therm Biol. 116:1036552023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Yang PC, He SH and Zheng PY: Investigation
into the signal transduction pathway via which heat stress impairs
intestinal epithelial barrier function. J Gastroenterol Hepatol.
22:1823–1831. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Li H, Chen H, Zhang S, Wang S, Zhang L, Li
J, Gao S and Qi Z: Taurine alleviates heat stress-induced mammary
inflammation and impairment of mammary epithelial integrity via the
ERK1/2-MLCK signaling pathway. J Therm Biol. 116:1035872023.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Cheng M, Yang Z, Qiao L, Yang Y, Deng Y,
Zhang C and Mi T: AGEs induce endothelial cells senescence and
endothelial barrier dysfunction via miR-1-3p/MLCK signaling
pathways. Gene. 851:1470302023. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Zhong J, Yu R, Zhou Q, Liu P, Liu Z and
Bian Y: Naringenin prevents TNF-alpha-induced gut-vascular barrier
disruption associated with inhibiting the NF-kappaB-mediated
MLCK/p-MLC and NLRP3 pathways. Food Funct. 12:2715–2725. 2021.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Huang Y, Luo X, Li X, Song X, Wei L, Li Z,
You Q, Guo Q and Lu N: Wogonin inhibits LPS-induced vascular
permeability via suppressing MLCK/MLC pathway. Vascul Pharmacol.
72:43–52. 2015. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|